The Number of Ransomware Attacks is Increasing Rapidly in 2021, How To Prevent Ransomware Attacks

In recent years, blackmail attacks have occurred frequently, and the number has increased year by year. It poses a serious threat to all walks of life, from financial institutions to higher education. As the new crown pneumonia pandemic has led to an increase in remote work, the number of ransomware attacks during the epidemic has increased by 148%. The following first takes everyone to quickly understand the important development trend of ransomware.

- Development of IT outsourcing services
The ransomware group has turned its attention to managed service providers (MSP), a platform that serves many customers at the same time. This means that if a hacker gains access to an MSP, it can also access the clients it serves. In most cases, MSP will be attacked by hackers due to the poor security of remote access tools.
- Attention turns to disadvantaged industries
Due to the pandemic, cyber attackers have been taking advantage of the worst-hit industries, such as the healthcare industry, municipalities, and educational institutions. These hackers also see the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of employees who now use personal devices to work remotely.
- The evolution of new ransomware and defenses
By 2021, the tactics used by ransomware and hackers to carry out attacks are evolving-but fortunately, defenses are evolving as well. In recent years, a new ransomware has been discovered, including:
Netwalker
The ransomware was created in 2019 by a cybercriminal organization called Circus Spider, allowing hackers to rent access to malware code in exchange for a certain percentage of funds received.
DarkSide
DarkSide is a recent organization whose ultimate goal is to steal and encrypt sensitive data, including backup via RaaS.
Conti
Conti ransomware uses dual ransomware technology to encrypt data on the infected machine. Attackers in this group usually send phishing emails from addresses trusted by the victims.
REvil: Also known as Sodin and Sodinokibi, REvil is a ransomware group known for extorting larger ransoms than competitors and promoting underground cybercrime forums.
- Spread to mobile devices
Hackers have been using mobile device features (such as emergency alerts and relaxation of permissions) to spread malware. Most mobile ransomware variants can cover every browser window or application with a ransom note, making the mobile device unusable.
- Ransomware as a service is increasing
Ransomware as a service is a subscription that allows affiliated companies to use ransomware tools that have been developed to perform ransomware attacks. It also allows them to expand their sphere of influence, and the decentralized nature of the attack makes it difficult for the authorities to stop the attack.
In addition, the creators of these tools will draw a certain percentage from each successful ransom payment. As the average ransom demanded by hackers has increased by 33% since the third quarter of 2019 ($11,605), affiliates withdraw as much as 80% from each payment.
Statistics about ransomware in specific industries
Ransomware attacks affect almost all enterprises of all industries and sizes. In 2019, nearly 56% of organizations in multiple industries reported ransomware attacks.
Health Care
Since 2009, the healthcare industry has reported more than 2,100 data breaches. (Technical Jury, 2021)
Healthcare organizations spend only 6% of their budgets on cybersecurity measures. (Intense healthcare, 2020)
In 2020, nearly 50% of healthcare data breaches are caused by ransomware attacks. (Health and Human Services, 2021)
The cost of an attack on health care is higher than any other industry, at $408 per record. (HIPAA Journal, 2020)
Since 2016, ransomware attacks targeting U.S. healthcare providers have caused more than $157 million in damages. (HIPAA Journal, 2020)
In 2020, 560 medical institutions were affected by ransomware attacks in 80 independent incidents. (Emsisoft, 2021)
Nearly 80 million people were affected by Anthem Breach in 2015, the largest healthcare data breach in history. (Wall Street Journal, 2015)
In 2016, 88% of ransomware attacks occurred in the United States. (Becker, 2016)
In September 2020 alone, cybercriminals infiltrated and stole 9.7 million medical records. (HIPAA Journal, 2020)
Educate
From 2019 to 2020, ransomware attacks against universities increased by 100%. (BlueVoyant, 2021)
The average cost of a ransomware attack in the higher education industry is $447,000. (BlueVoyant, 2021)
Since 2020, 1,681 higher education institutions have been attacked by 84 ransomware attacks. (Emsisoft, 2021)
66% of universities lack basic email security configuration. (BlueVoyant, 2021)
38% of the universities analyzed in the Higher Education Network Security Report have insecure or open database ports. (BlueVoyant, 2021)
In 2020, cyberattacks on K-12 schools have increased by 18%. (K-12 Cyber Security, 2020)
After the ransomware attack occurred in April 2018, a school district in Massachusetts paid $10,000 in Bitcoin. (Cyber scoop, 2018)
Finance and Insurance
Of all the records leaked in 2019, 62% came from financial institutions. (Bit Glass, 2019)
More than 204,000 people have experienced login attempts to access their banking information. (Hub Security, 2021)
90% of financial institutions have become the target of ransomware attacks. (Public Relations Distribution, 2018)
Small financial institutions with revenues of less than US$35 million are facing increasing threats. (National Credit Cooperative Administration, 2019)
In 2020, 70% of 52% of attacks against financial institutions came from Kryptik Trojan malware. (Hub Security, 2021)
LokiBot’s goal is more than 100 financial institutions with revenues of more than 2 million U.S. dollars. (Hub Security, 2021)
Between March and June 2020, phishing and ransomware attempts by banks increased by 520%. (American Banker, 2020)
Government
In 2020, 33% of government agency attacks are ransomware (Security Intelligence, 2020)
In June 2019, a city in Florida paid a ransom of $600,000 to restore hacked files. (CBS News, 2019)
Only about 38% of local and state government employees have received training in the prevention of ransomware attacks. (IBM, 2020)
In 2020, ransomware attacks targeting southern cities caused more than 7 million U.S. dollars in damage. (SC Magazine, 2020)
In 2019, a ransomware attack hit a city on the east coast, causing more than $18 million in damage. (Baltimore Sun, 2019)
In 2019, 226 mayors in 40 U.S. states agreed to an agreement that refused to pay ransoms to cybercriminals. (Hash, 2020)
In 2019, attacks on municipalities increased by 60% from the previous year. (Kaspersky Lab, 2019)
The hottest cyber security incidents in 2019 were ransomware attacks against state and local governments. (Government Technology, 2019)
From 2013 to 2018, 48 of the 50 U.S. states were affected by at least one ransomware attack. (Bank Information Security, 2019)

Mobile ransomware statistics
With the increase in dependence on mobile phones, especially the use of personal mobile devices in the workplace, the risk of ransomware attacks also increases. In the workplace, employees may access sensitive information from their mobile devices via company WiFi and generally insecure networks. This exposes users and their organizations to huge vulnerabilities that can be exploited. Check out some WiFi safety tips to prevent being a victim of hackers.
More than 68,000 new mobile ransomware Trojans were discovered in 2019. (Hashed Out, 2020)
In 2017, mobile malware variants increased by 54%. (Symantec, 2018)
The phones of more than 4.2 million US mobile users have been attacked by ransomware. (Kaspersky, 2020)
In 2018, Symantec detected more than 18 million mobile malware instances. (Symantec, 2018)
Less than 20% of mobile malware is spread through browsers. (The State of RSA Cybercrime, 2019)
In 2018, 60,176 mobile ransomware Trojans were detected among 80,638 users in 150 different countries. (Kaspersky, 2018)
There are more than 4,000 mobile threat variants and families in the McAfee sample database. (McAfee, 2021)
In 2018, more than 8,000 installations of mobile banking ransomware Trojans were detected. (Kaspersky, 2018)
In just 30 days, 900,000 Android phones were attacked by ScarePackage ransomware. (KnowBe4, 2020)
Ransomware cryptocurrency statistics
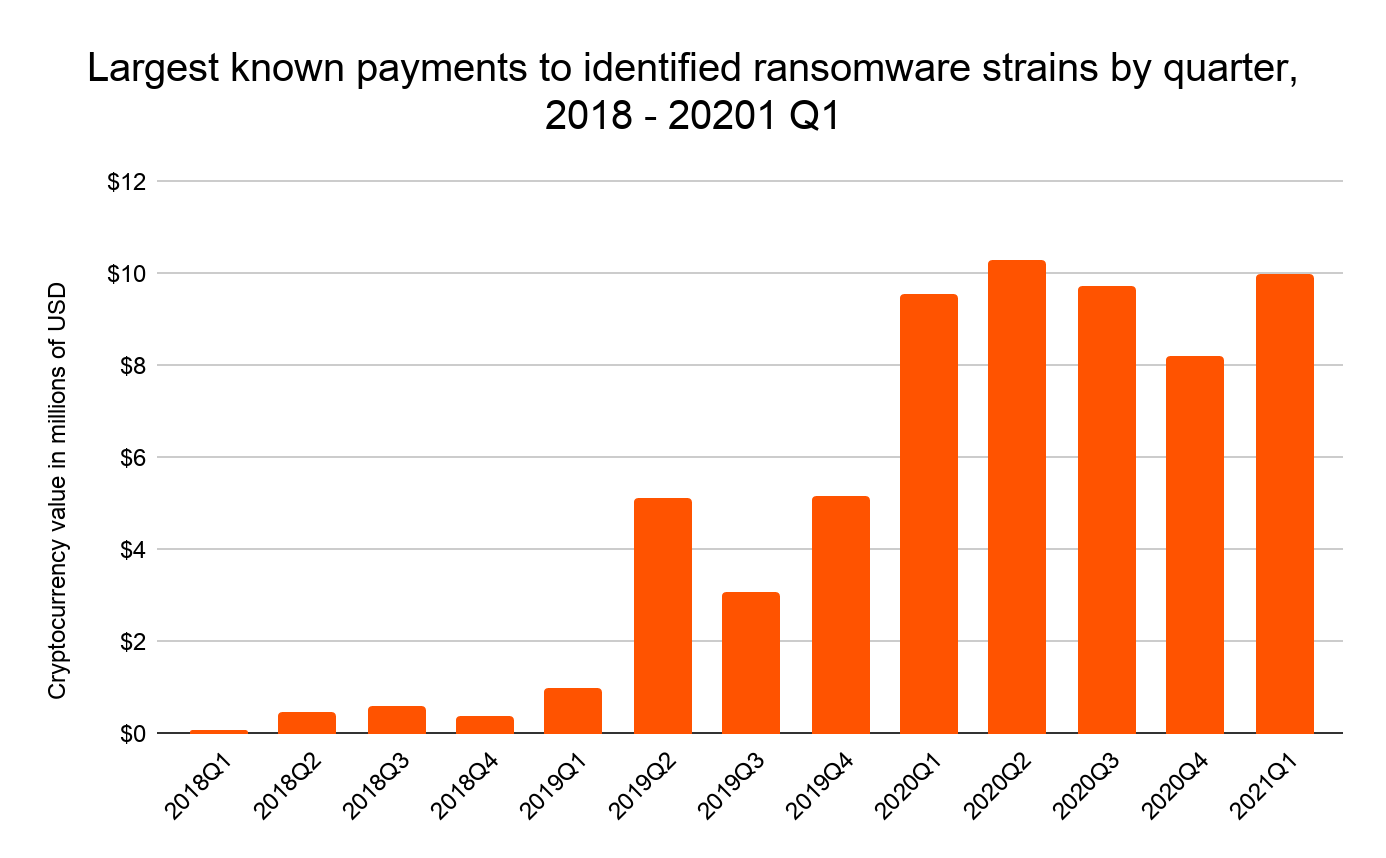
Since the birth of Bitcoin, the world’s first cryptocurrency, the efficiency of transferring funds and data has become more and more efficient. As of 2021, there are more than 4,000 different types of cryptocurrencies. With the advancement of digital and financial technology, new threats to network security have surfaced.
In June 2020, a university on the West Coast paid cybercriminals $1.14 million in Bitcoin after being attacked by ransomware. (BBC News, 2020)
In 2017, 95% of the ransom was cashed through the Bitcoin platform BTC-e. (Beep Computer, 2017)
In 2020, ransomware payments accounted for 7% of all funds received by cryptocurrency addresses. (Chain Analysis, 2020)
Hackers who attacked oil companies earned more than $90 million in Bitcoin. (Business Insider, 2021)
Cryptocurrency transactions can be traced back to individuals 60% of the time. (MIT Technology Review, 2017)
In 2019, illegal activities accounted for 2.1% of all cryptocurrency transactions or transfers worth approximately US$21.4 billion. (Chainalysis, 2021)
The cost of being attacked by ransomware

Ransomware attacks are costly (whether financial or your reputation)-companies worldwide that have been attacked by ransomware have spent approximately US$144.2 million to address the impact of the attack. Here are some statistics covering the cost of ransomware attacks.
The value of ransom demands has increased, with some demands exceeding $1 million. (Bureau of Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security, 2021)
The cost of a ransomware attack in 2019 exceeded US$7.5 billion. (Emsisoft, 2019)
In 2021, the average expenditure of medium-sized organizations is $170,404. (Sophos, 2021)
In May 2021, the CEO paid the hacker $4.4 million in Bitcoin after receiving the ransom note. (The Wall Street Journal, 2021)
In the first quarter of 2017, FedEx lost approximately US$300 million due to the NotPetya ransomware attack. (Online exclusive news, 2021)
The average cost of recovering from a ransomware attack is $1.85 million. (Sophos, 2021)
The losses caused by ransomware attacks in 2017 exceeded US$5 billion-
15 times this. (Cyber Security Venture Capital Company, 2017)
The cost of downtime increased by 200% year-on-year (2019 compared to 2018). (Dato, 2019)
On average, ransomware attacks cause 15 working days of downtime. Because of this inactivity, the company loses approximately $8,500 per hour. (Health IT Security, 2020)
The ransomware attacking an unnamed oil and gas company cost $30 million. (Dato, 2017)
According to reports, the hacker group behind the oil company’s attack received a ransom of US$90 million from approximately 47 victims in just nine months. (Fox Business, 2021)
The number of companies reporting ransom payments is four times the number of more than 100 employees affected by the ransomware attack. (Secret Reading Survey, 2020)
Forecast and future development trend of ransomware
Ransomware is an increasingly serious problem in the field of network security and continues to affect the world today. Looking ahead, here are some statistics covering ransomware forecasts and future trends.
The total cost of ransomware is expected to exceed US$20 billion in 2021. (Cybercrime Magazine, 2019)
Cyber security Ventures predicts that ransomware will cost $6 trillion a year. (Cyber Security Venture Capital Company, 2020)
In the future, due to the vulnerability of identity-based threats, more organizations will turn to a zero-trust security model. (RSA Security, 2020)
Teleworkers will become the main target of cyber criminals throughout 2021. (Security Magazine, 2020)
Even after the COVID-19 restrictions are lifted, 84% of organizations still use remote work as the norm, resulting in an increase in Internet users and a greater risk of data leakage. (Bit Glass, 2020)
Future hackers will target full-time employees because personal devices are more susceptible to hacking than office hardware. (Safety Magazine, 2020)
How to prevent ransomware attacks

Make sure you take steps to prevent attacks and data loss within your organization. Here are some effective ways to prevent ransomware from affecting your company.
Educate your employees
Use in-company security training to help your employees better understand cyber security and its importance. Implementing this training will help ensure a more cyber-resilient work culture.
Avoid clicking on suspicious links
Be careful to open or click attachments or links from spam or unsolicited emails. According to Verizon’s 2018 Data Breach Investigation Report, phishing involves 70% of data breaches. To avoid this situation, it is helpful to know how to spot phishing scams.
Use email and endpoint protection
Be sure to scan all emails and filter malicious attachments and links, and use the latest malware signatures to keep your firewall and endpoint detection software up to date. You should also notify users of e-mails outside the network and provide a VPN for users to use outside the network.
Use mobile phone encryption protection products
When protecting company assets, mobile phone information security is of paramount importance. We usually use the Wibo key to encrypt the dual Type-c U disk, which can effectively protect the data security of the mobile phone. The product is equipped with an A5 security chip, which implements hardware-level encryption protection for mobile phones, and can be used by Android phones with a Type-C interface. Important files are encrypted and stored with one key, so there is no fear of being attacked by ransomware. It is recommended that you develop the habit of regular backup, and prepare an extra Micro Platinum key encrypted dual Type-c U disk at home to prevent loss of important data, safe and reliable.
To combat data leakage, you must use the hardware-level encryption tool for mobile phone hardware-level encryption of the dual Type-c U disk encryption with Microplatin key to truly escort your information security in all aspects!
Colonial Pipeline Paid 5 Million Dollar Ransom to Hacker for their Data and Services Restore