Top OSINT tools: find sensitive public information before hackers

Top OSINT tools: find sensitive public information before hackers
Top OSINT Tools: Hackers use open source intelligence to find information that can help them break into the system. Use these tools to see how much such information is exposed.
In the 1980s, the military and intelligence agencies began to transform certain information-gathering activities from covert operations such as reading opponents’ letters or tapping phone calls to discovering hidden secrets. A lot of work has been devoted to finding useful information that is publicly available or even officially released.
The world was undergoing tremendous changes at the time. Even if social media had not yet appeared, there were various sources of information, such as newspapers and publicly available databases, containing interesting and even useful information, especially when it came to knowing how to connect dots to get a comprehensive overview. In the eyes of people. This type of spy secret is named Open Source Intelligence (OSINT).
How OSINT is applied in the security field
The OSINT technology used by spies can now also be applied to the field of network security. Most companies and enterprises have a huge public-facing infrastructure that spans multiple networks, technologies, hosting services, and namespaces. Information can be stored on employee desktop computers, legacy on-site servers, employees’ own BYOD devices, the cloud, embedded in devices such as network cameras, or even hidden in the source code of active applications and programs.
In fact, IT employees of large companies are basically unable to know all the assets of their own companies, regardless of whether the assets are public or not. In addition, many companies indirectly own or control multiple additional assets, such as their social media accounts. In this way, there may be a lot of information that will bring great risks if it falls into the wrong hands.
As a result, new OSINT tools came into being. Despite their respective biases, such tools basically have three functions.
- Discover public assets
The most common function of this type of tool is to help IT teams discover public assets and map the information that these assets hold that can form a potential attack interface. Basically, these tools will not find program vulnerabilities or perform penetration tests. Its main job is to record the information that can find or understand company assets without hacking.
- Discover relevant information outside the company
The second function performed by the OSINT tool is to find relevant information outside the company, such as posting on social media or strictly defining a domain or location outside the network. After many mergers and acquisitions, companies and enterprises that continue to merge and merge their company’s IT assets will find this feature very useful. Given the rapid growth and popularity of social media, finding sensitive information outside of company boundaries may be useful for any organization.
- Organize the information found into a feasible table
Finally, some OSINT tools help to sort the discovered information into useful feasibility intelligence. An OSINT scan performed by a large enterprise may produce millions of results, especially when the scan options include both internal and external assets. It is undoubtedly very helpful if all the data can be assembled and the most urgent issues can be dealt with first.
Top OSINT tools
Choosing the right OSINT tool helps to discover information about the company, employees, IT assets, and other credentials or sensitive data that can be used by attackers, and can improve the company’s network security status. Hidden or removed after discovering such information can reduce various attacks from phishing to denial of service.
Below is a list of several top-level tools for OSINT (in no particular order), describe their respective areas of expertise, explain the characteristics that distinguish them from other tools, and describe the specific value that each can bring to the company’s network security work.
- Maltego
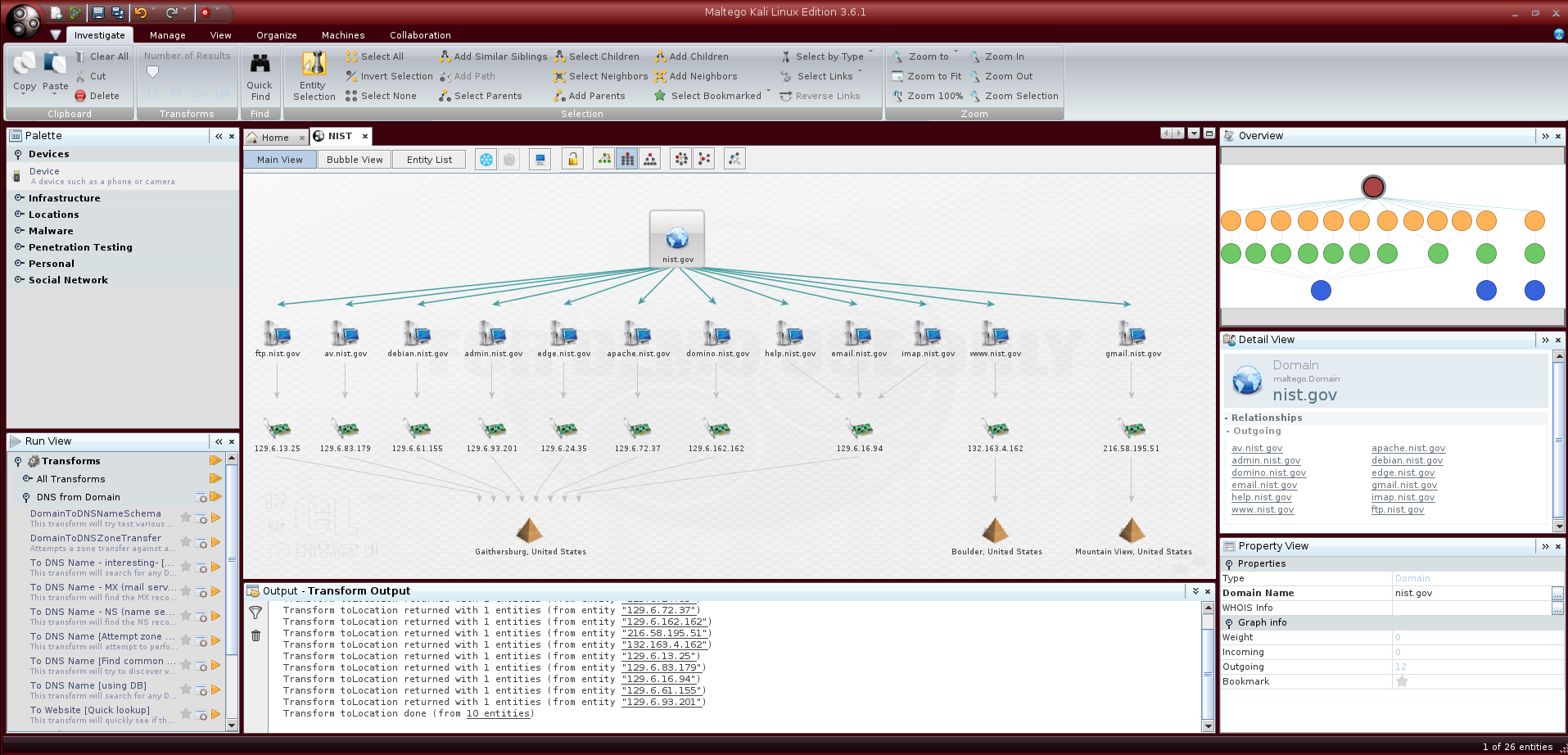
Maltego is good at discovering relationships between people, companies, domains, and publicly accessible information on the Internet. The tool is also known for ingesting a large amount of discovered information and presenting it in intuitive and easy-to-understand charts. These charts perform well in transforming raw intelligence into actionable intelligence, and each chart can have up to 10,000 data points.
Maltego automatically searches different public data sources, so users can execute multiple queries with one click. The program refers to the search plan as a “conversion operation,” and by default, it sets many plans containing common public information sources, such as DNS records, Whois records, search engines, and social networks. Because the search is performed using a public interface, the program is compatible with any information source with a public interface, so it is very convenient to add more searches to the conversion operation or to build a new conversion operation.
After the information is collected, Maltego will associate the information to reveal hidden relationships among names, email addresses, aliases, companies, websites, document owners, subsidiaries, and other information, to assist in investigations, or to find potential problems. Maltego is a Java program, compatible with Windows, Mac, and Linux platforms.
The lite version called Maltego CE is free. The desktop version of Maltego XL is $1,999 per instance. The server installation version for large-scale commercial use starts at $40,000, with a full set of training programs.
Home Page: https://www.maltego.com/\
2. Recon-ng
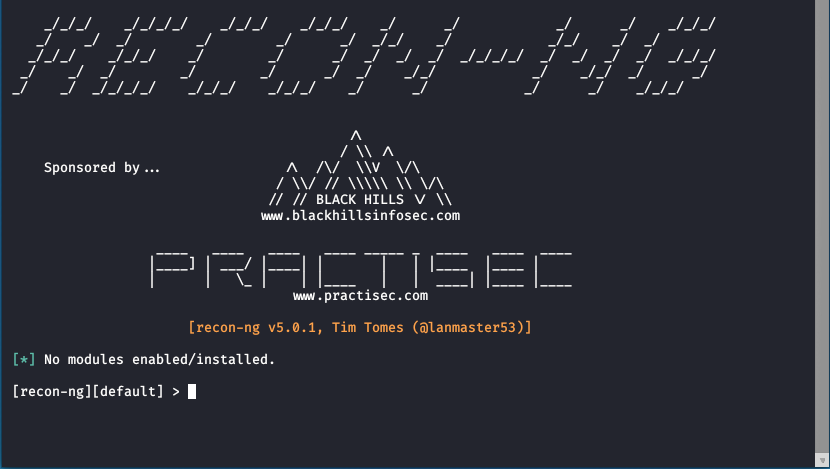
Recon-ng is a Python program, and the interface is very similar to the famous Metasploit Framework. Those who have used Metasploit should be able to get started soon. The program also has interactive help functions that many Python modules lack, and the learning time for developers should not be too long.
Recon-ng automates many time-consuming OSINT operations, such as cut and paste. Although it does not claim that all OSINT collection operations can be performed, Recon-ng can be used to automate most mainstream information collection, leaving more time for events that still require manual processing.
Recon-ng uses a modular framework with a large number of built-in features, enabling even the most junior Python developers to create publicly available data searches and return high-quality results. Common tasks such as standardized output, database interoperability, sending web requests, and managing API keys can all be found in the interface. Developers do not need to program to perform searches, just select the functions they want to perform, and an automated module can be built within a few minutes.
Recon-ng is free and open-source software. There is a guide to using this tool on the wiki, as well as a detailed introduction to its best practices.
Home Page: https://github.com/lanmaster53/recon-ng
3. theHarvester

theHarvester is the simplest tool on this list, designed to capture public information that exists outside the company’s own network. This tool can also find unexpected events on the internal network, but its main purpose is still external. It is also effective for the reconnaissance step before penetration testing or similar exercises.
The information sources used by theHarvester include common search engines such as Bing and Google, as well as lesser-known metadata engines such as dogpile, DNSdumpster, and Exalead. Netcraft Data Mining and AlienVault Open Threat Exchange are also used for it. theHarvester can even use the Shodan search engine to find open ports on discovered hosts. In general, theHarvester tool collects email, name, subdomain, IP, and URL.
TheHarvester can access most open sources without special preparation. However, some sources require API keys. In addition, the minimum environment requirement is Python 3.6.
Anyone can get theHarvester on GitHub. It is recommended to use the virtualenv command to create a separate Python environment when cloning.
Home Page https://github.com/laramies/theHarvester
4. Shodan

Shodan is a dedicated search engine that finds information about billions of IoT devices. These devices are usually not searchable but are now found in every aspect of life. The Shodan search engine can also be used to find open ports and vulnerabilities on the target system. Some other OSINT tools, such as theHarvester, use Shodan as a data source, although in-depth interaction with Shodan requires a paid account.
The number of locations that Shodan can monitor and search is surprising. It is one of the few search engines that can check operational technology (OT), and can be used to detect industrial control systems in places such as power stations and manufacturing plants. If there is no tool like Shodan, there will be a big missing piece in the implementation of OSINT collection for industries that have deployed both IT and OT technologies.
In addition to IoT devices such as cameras, building sensors, and security devices, Shodan can also check things like databases to see if there are other publicly available channels to obtain information from them besides the main interface. Shodan can even be used in video games to discover the “Minecraft” and “Counter-Strike: Global Offensive” servers hidden on the corporate network to see what vulnerabilities are generated.
Anyone can purchase a freelancer license, which can scan up to 5,120 IP addresses per month and return up to 1 million results. It is priced at $59 per month. The maximum number of IP addresses scanned by the enterprise license is 300,000 per month, and the number of returned results is unlimited. The Enterprise Edition costs US$899 per month and includes vulnerability search filters and advanced support.
Home Page: https://www.shodan.io/
5. Metagoofil
Another freely available tool on GitHub optimizes the extraction of public document metadata. Metagoofil can investigate almost any document type accessible through public channels, including .pdf, .doc, .ppt, .xls, etc.
The amount of interesting data that Metagoofil can collect is staggering. The search returns include the usernames associated with the documents found, and sometimes the real names if available. The tool can also draw a road map to access these documents, and provide the server name of the document hosting company, shared resources, and directory tree information.
Everything Metagoofil finds is useful to hackers, who can launch password brute force attacks or email phishing attacks. Companies that want to protect themselves can also use the same OSINT information to protect or hide it before malicious hackers take action.
Home Page: https://github.com/laramies/metagoofil
6.searchcode
If you need to truly explore OSINT to collect complex matrices, searchcode is a highly specialized search engine for finding useful information in source code. Surprisingly, such a powerful engine is only a masterpiece of a developer.
Because you need to add a codebase before you can search for programs, searchcode actually crosses the boundary between OSINT tools and non-public information search tools. However, because developers can find problems with sensitive information in the code of the application in use or application under development, searchcode can still be regarded as an OSINT tool. For applications under development, these problems can be fixed before the application enters the production environment from the development stage.
Although any problem involving code requires a little bit more knowledge than Google search, searchcode does a good job of making the interface as simple and easy to use as possible. Users only need to enter their search fields, and the searchcode will return the relevant results, highlighting the keywords to be searched in the code line. Recommended searches include usernames, eval $_GET calling security vulnerabilities, redundant functions such as re.compile, and special characters that can be used to trigger code injection attacks.
Most of the time, the results returned by searchcode are self-explanatory. However, if necessary, you can also screen carefully to find deeper information or matching problems.
Home Page: https://searchcode.com/
Plug open-source intelligence loopholes
Not every hacking incident or intrusion involves advanced persistent threats or complex deep penetrations. Like most, hackers also like to take the simplest path to achieve their goals. If the information you want can be obtained through open channels, why spend months of hard work to break through the tight network security defenses? At the very least, sensitive information can be used as a shortcut to obtain valid credentials or to help plan effective intrusions with a smaller workload or risk.
OSINT tools can help companies understand what information about themselves, their own networks, data, and users is publicly available. Finding out this information quickly can be deleted before hackers use it to protect the company’s network security. These tools can be regarded as powerful thrusters in offensive and defensive competition.