Wireshark Tutorial: Network & Password Sniffer

Wireshark Tutorial: Network & Password Sniffer
Computers use the network to communicate. These networks can be located on the local area network LAN or exposed to the Internet. A network sniffer is a program that captures low-level packet data transmitted over the network. Attackers can analyze this information to discover valuable information, such as user IDs and passwords.
In this article, we will introduce you to common network sniffing techniques and tools used to sniff the network. We will also study the countermeasures that can be taken to protect sensitive information transmitted over the network.
What is Network sniffing?
Computers communicate by broadcasting messages on the network using IP addresses. After sending a message on the network, the recipient computer with a matching IP address will respond with its MAC address.
Network sniffing is the process of intercepting data packets sent over the network. This can be done through dedicated software programs or hardware devices. Sniffing can be used;
- Capture sensitive data, such as login credentials
- Eavesdrop on chat messages
- The capture file has been transferred over the network
The following are protocols that are easily sniffed
- Remote login
- Rlogin
- HTTP
- SMTP
- NNTP
- Pop music
- FTP
- IMAP
If the login details are sent in clear text, the above protocol is vulnerable to attack
Passive and active sniffing
Before discussing passive sniffing and active sniffing, let us look at the two main devices used for networked computers. Hubs and switches.
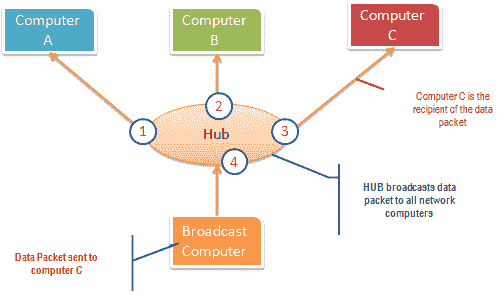
The hub works by sending broadcast messages to all output ports on it ( except the port that sends the broadcast ). If the IP addresses match, the recipient computer responds to the broadcast message. This means that when using a hub, all computers on the network can see the broadcast message. It runs on the physical layer (layer 1) of the OSI model.
The following figure illustrates how the hub works.
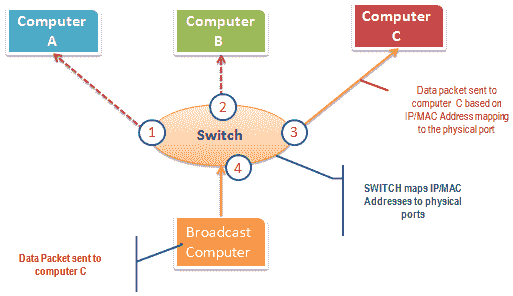
The switch works differently; it maps the IP/MAC address to the physical port on it. Send the broadcast message to the physical port that matches the IP/MAC address configuration of the recipient’s computer. This means that the broadcast message is only seen by the recipient’s computer. The switch operates at the data link layer (layer 2) and the network layer (layer 3).
The figure below illustrates how the switch works.
Passive sniffing is intercepting data packets transmitted through the network using a hub. It is called passive sniffing because it is difficult to detect. Since the hub sends broadcast messages to all computers on the network, it is also easy to implement.
Active sniffing is intercepting data packets transmitted through the network using the switch. There are two main methods for sniffing the exchanged link network, namely ARP poisoning and MAC flooding.
Hacking activity: sniffing network traffic
In this actual situation, we will use Wireshark to sniff packets transmitted through the HTTP protocol. For this example, we will use Wireshark to sniff the network and then log in to a web application that does not use secure communication. We will log in to the web application on http://www.techpanda.org/
Login to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need to enable JavaScript to view it. , The password is Password2010.
Note: We will log into the web application for demonstration purposes only. This technology can also sniff data packets sent by other computers on the same network as the computer used for sniffing. Sniffing is not limited to techpanda.org but also sniffs all HTTP and other protocol packets.
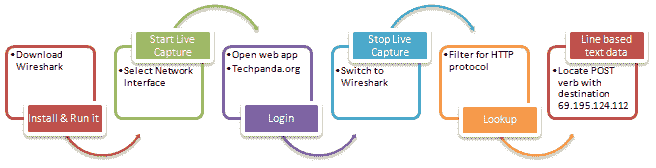
Use Wireshark to sniff the network
The figure below shows you the steps to be taken to complete this exercise without causing confusion
Download Wireshark from this link http://www.wireshark.org/download.html
- Open Wireshark
- You will get the following screen
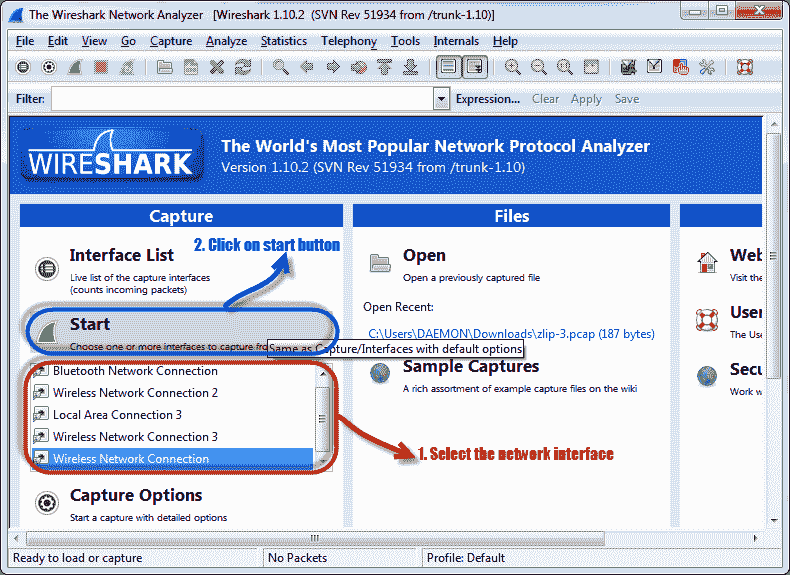
- Select the network interface you want to sniff. Please note that in this demo, we are using a wireless network connection. If you are on a LAN, you should choose the LAN interface.
- Click the start button, as shown in the picture above
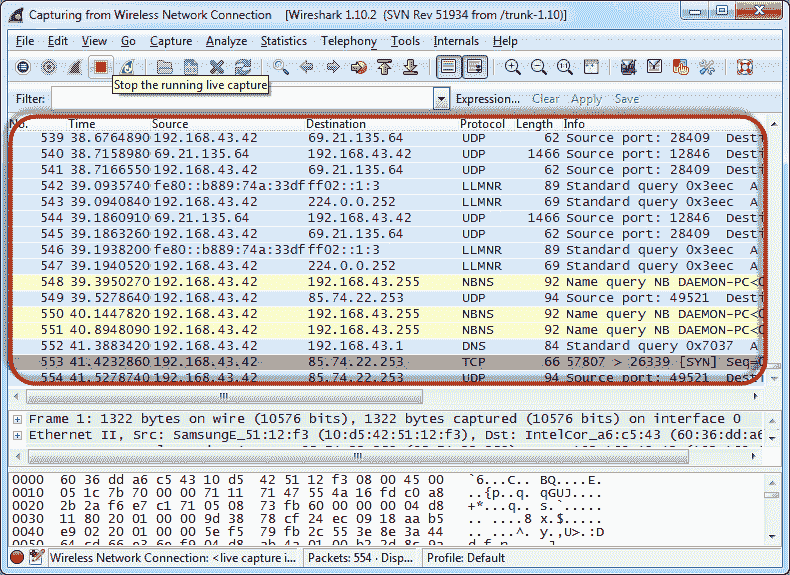
- Open the web browser and enter http://www.techpanda.org/
- Login Email to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need to enable JavaScript to view it. , The password is Password2010
- Click the submit button
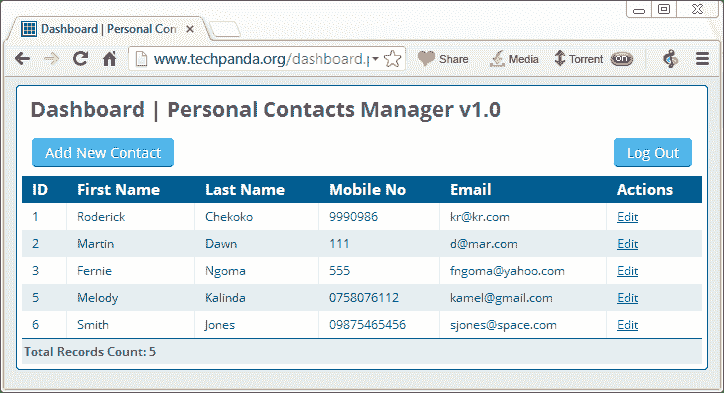
- Successful login should provide you with the following information center
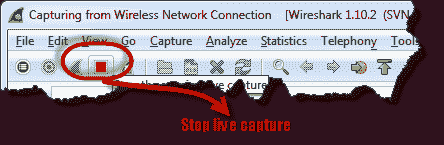
- Return to Wireshark and stop real-time capture
- Only use the filter text box to filter the HTTP protocol results
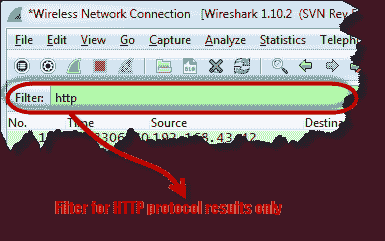
- Find the entry with the HTTP verb POST in the “Information” column and click on it
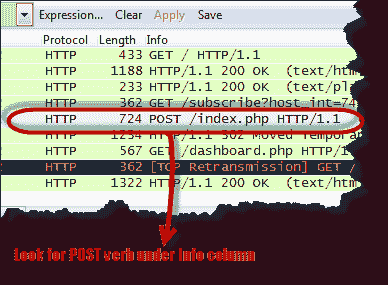
- Below the log entry, there is a panel that contains a summary of the captured data. Find a summary that says line-based text data: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
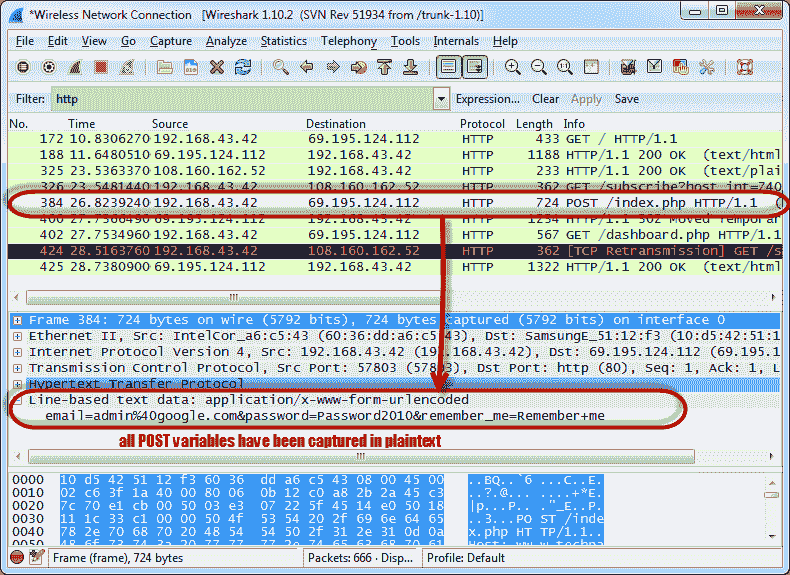
- You should be able to view the plain text values of all POST variables submitted to the server via the HTTP protocol.
What is MAC flooding?
MAC flooding is a network sniffing technology that floods the switch’s MAC table with fake MAC addresses. This overloads the swap memory and makes it act as a hub. Once the switch is threatened, it will send broadcast messages to all computers on the network. In this way, you can sniff the packets sent on the network.
Countermeasures to prevent MAC flooding
- Some switches have port security features. This function can be used to limit the number of MAC addresses on the port. In addition to the address table provided by the switch, it can also be used to maintain a secure MAC address table.
- Authentication, authorization, and accounting servers can be used to filter the discovered MAC addresses.
Sniffing countermeasures
- Restrictions on network physical media greatly reduce the chance of installing a network sniffer
- Encrypting messages while transmitting over the network greatly reduces their value because they are difficult to decrypt.
- Changing the network to a Secure Shell (SSH) network can also reduce the chance of sniffing the network.
Summary
- Network sniffing is intercepting packages because they are transmitted over the network
- Passive sniffing is done on the network using a hub. It is difficult to detect.
- Active sniffing is done on the network using the switch. It is easy to detect.
- MAC flooding is achieved by flooding the MAC table address list with fake MAC addresses. This makes the switch work as a hub
- The security measures outlined above can help protect the network from sniffing.
WATCH MORE NEWS CLICK THE LINKS
Researchers Break Intel SGX With New ‘SmashEx’ CPU Attack Technique
Common Methods And Test Methods Of SQL Injection Attacks