Windows Servers are Vulnerable to Remote Code Execution due to a Recent PHP Vulnerability

Windows Servers are Vulnerable to Remote Code Execution due to a Recent PHP Vulnerability
Several details have surfaced regarding a newly discovered major security hole that affects PHP. This flaw has the potential to be exploited in order to gain remote code execution under specific conditions.
The vulnerability, which has been identified as CVE-2024-4577, has been defined as a CGI argument injection vulnerability that affects all versions of PHP that are installed on the Windows operating system.
In accordance with the findings of a security researcher from DEVCORE, the vulnerability makes it feasible to circumvent the safeguards that have been implemented to address another security weakness known as CVE-2012-1823.
According to Orange Tsai, a security researcher, “the team did not notice the Best-Fit feature of encoding conversion within the Windows operating system while they were implementing PHP.”

Due to this error, it is possible for attackers who have not been authenticated to circumvent the prior security provided by CVE-2012-1823 by using particular letter sequences. Through the use of the argument injection technique, it is possible to execute arbitrary code on remote PHP servers.
As a result of the vulnerability being disclosed in a responsible manner on May 7, 2024, a patch has been made available for PHP versions 8.3.8, 8.2.20, and 8.1.29.

XAMPP installations on Windows that are configured to use the locales for Traditional Chinese, Simplified Chinese, or Japanese are vulnerable by default, according to a warning issued by DEVCORE.
Mod-PHP, FastCGI, or PHP-FPM are some of the more secure alternatives that Taiwanese business administrators use instead of the antiquated PHP CGI. The company is also proposing that administrators switch away from the obsolete PHP CGI entirely.

“This vulnerability is incredibly simple, but that’s also what makes it interesting,” Tsai explained to reporters. “Who would have thought that a patch, which has been reviewed and proven secure for the past 12 years, could be bypassed due to a minor Windows feature?”
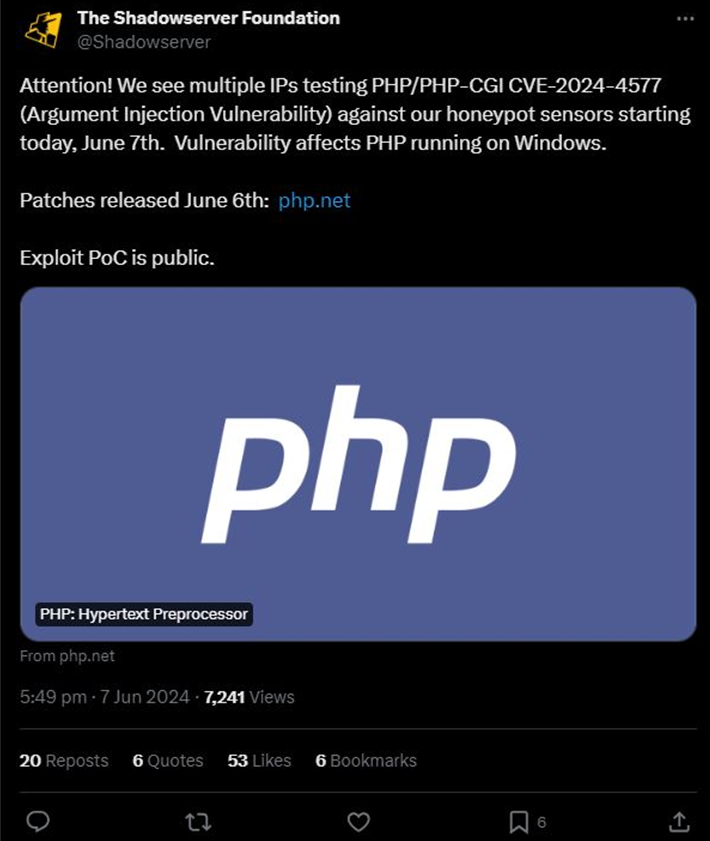
The Shadowserver Foundation stated in a post that was shared on X that it has already discovered efforts to exploit the vulnerability against its honeypot servers within twenty-four hours of the vulnerability being made public that it was discovered.
In light of the fact that watchTowr Labs has reported that it has been successful in developing an exploit for CVE-2024-4577 and achieving remote code execution, it is vital that users react fast to apply the most recent patches.

Described by security researcher Aliz Hammond as “a nasty bug with a very simple exploit.”
“Those running in an impacted setting under one of the affected locales – Chinese (simplified, or traditional) or Japanese – are encouraged to do this as fast as humanly possible, as the bug has an excellent chance of being abused en-mass due to the low exploit complexity.”
About The Author:
Yogesh Naager is a content marketer who specializes in the cybersecurity and B2B space. Besides writing for the News4Hackers blog, he’s also written for brands including CollegeDunia, Utsav Fashion, and NASSCOM. Naager entered the field of content in an unusual way. He began his career as an insurance sales executive, where he developed an interest in simplifying difficult concepts. He also combines this interest with a love of narrative, which makes him a good writer in the cybersecurity field. In the bottom line, he frequently writes for Craw Security.
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE