Analysis of Ranion Ransomware

Analysis of Ranion Ransomware
Analysis of Ranion ransomware that has been running for four years
Affected platforms: Microsoft Windows
Affected: Windows users
Impact: Encrypt the files on the attacked device and ask the victim to pay a ransom to recover the encrypted files.
Severity: high
Ranion is a ransom as a service (RaaS). Since it has been active since at least February 2017, there are quite a few iterations of it. Although its activity and purpose is to encrypt files on the compromised device and obtain ransom from users to recover their files, which makes it look the same as other ransomware, the truth is that the internal workings of Ranion RaaS are the same as other ransomware. The software is very different.
The life cycle of each version of ransomware is usually very short. For example, some of the most famous ransomware campaigns in 2021 include:
Has disappeared:
REvil (also known as Sodinokibi), which has been active since 2019, has disappeared;
Avaddon ransomware;
Ragnarok ransomware;
Darkside ransomware;
FonixCrypter ransomware abandoned criminal activities in January and released the decryption tool and its master decryption key;
The latest:
In July, advertisements for Black matter ransomware appeared on underground online forums. Although the Black matter is not an iteration of another ransomware, there are rumors that it is related to Darkside;
Haron ransomware debuted in July, based on Thanos and Abaddon ransomware development;
Doppelpaymar ransomware was renamed Grief (PayOrGrief);
SynAck ransomware was renamed El_Cometa in August;
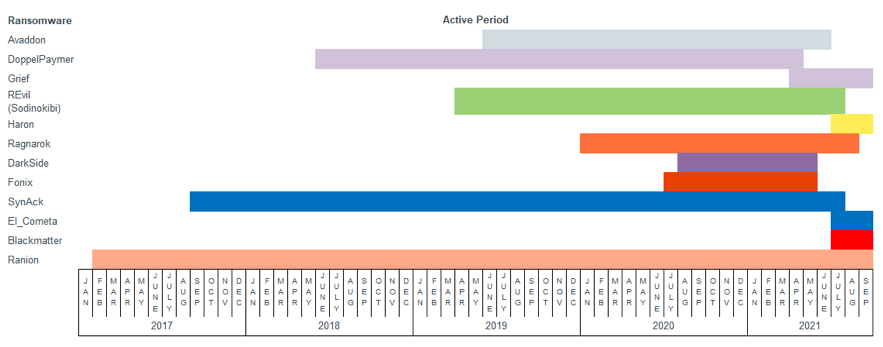
The ransomware listed above (disappeared or renamed in 2021) has an average lifespan of less than two years. The reasons for stopping operations vary by ransomware group, but they usually do so to avoid law enforcement and security researchers.
Ranison ransomware has been active for four years
The Ranion ransomware variant recently discovered by FortiGuard Labs runs counter to this trend. The Ranison ransomware family seems to have existed at least in early 2017, giving it a lifespan of more than four years. In February of the same year, Daniel Smith of Radware Security Company disclosed Ranion ransomware for the first time and described it as “ransomware as a service.” Surprisingly, its website on the dark web remains relatively unchanged. The developers of Ranion still claim that Ranion was created for educational purposes and ask users not to use the ransomware for illegal activities.
The latest version of Ranion, version 1.21, was released in July 2021. Surprisingly, Ranion developers will update the ransomware every month in 2021 (except May), including updates for detection and evasion, which makes people suspect that the ransomware is used for educational purposes. Another interesting data point is that version 1.08 was released at least in January 2018 and only updated 7 times in 35 months (January 2018-December 2020). However, in 2021, its development speed accelerated rapidly, and in 7 months, it was updated 6 times for unknown reasons. Every update in 2021 includes additional code that uses an open-source program called ConfuserEx to evade detection and protect the identity of the security vendor.
Introduction to Ranion RaaS

The latest version of Ranion ransomware is designed to use the following 44 file extensions to encrypt files on the compromised device. Compared with the previous analysis, five new file types have been added (the newly added extensions are highlighted in orange):
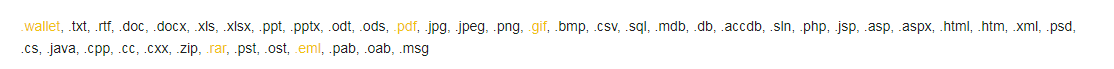
Although the ransomware is not designed to encrypt executable files, Ranion developers stated that users can request to encrypt other file types/extensions for free, as any file may become the target of Ranion ransomware.
Ranion’s business strategy
As early as 2017, Ranion provided users with two support packages (1 year and 6 months of service). Today, the Ranion team offers four support packages: Elite, Advanced, Standard, and Test.
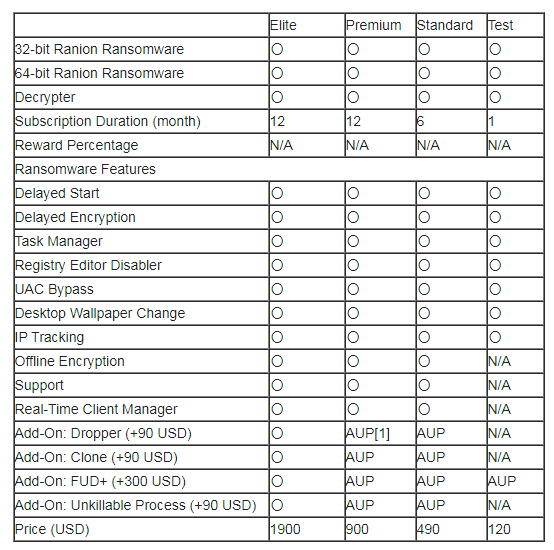
Previously, the most expensive package was 0.95 Bitcoin, and the cheapest package was 0.60 Bitcoin. In February 2017, a Bitcoin was worth about 1,200 USD, which means that the prices of these packages were about 1,140 USD and 720 USD, respectively. As of September 2021, one Bitcoin exchanged approximately $50,000, so Ranion developers adjusted the price, and now they also offer discounts for additional options that are easy to purchase.
Ranion’s business model is very different from other RaaS vendors. Typically, ransomware-as-a-service providers pay 60%-80% of the ransom to “affiliated companies” that have successfully installed their ransomware on the victim’s device. Ranion developers do not accept the sharing of intermediaries. Instead, their affiliates pay for RaaS services in advance, and then they receive 100% of the ransom. Although some RaaS vendors try to recruit experienced affiliates and often screen potential affiliates before allowing them to sign up for the service, Ranion developers have not. This is one of the reasons why many inexperienced affiliates start from Ranion because of the lower barriers to entry.
To understand how this model works, we tracked some Bitcoin wallets that an older Ranion sample used to pay the ransom. Within a week after the Ranion sample was provided, two payments were made to the wallet, totaling approximately $153 and $460 in Bitcoin. But one bitcoin wallet used by Ranion records transactions from two other bitcoin wallets. Bitcoin worth approximately $4.7 million was transferred from more than 300 different Bitcoin wallets to one of the wallets.
dropper plugin
Another notable feature of Ranion is that it provides buyers with the opportunity to purchase dropper add-ons. At first glance, “dropper” may sound like a malware plug-in that Ranion affiliates can use to provide ransomware, but this is not the case. According to the FAQ on the purchase website, the description of this plug-in is as follows: “RANION can download a program (exe file) of yours and execute it after the encryption process is over.”
For example, an attacker may use this add-on to silently download and install the remote access tool “RAT” on a Ranion-infected victim’s computer. Even if the victim chooses to pay the ransom, Ranion decryption program will only decrypt encrypted files, but will not delete the RAT. Then, Ranion affiliates can turn to other RaaS services that are willing to purchase access to existing businesses (such as Lockbit 2.0 and Blackmatter RaaS) and sell the victimized victims for additional profits.

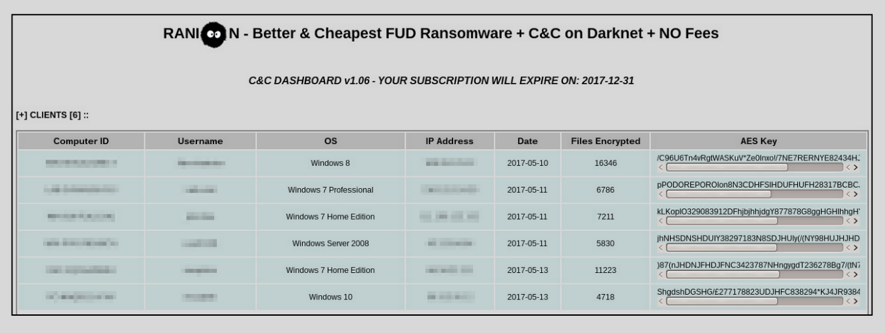
Ranion ransomware spread
The spread method of Ranion ransomware recently observed by FortiGuard Labs is very simple. It is done through spear-phishing emails with zip file attachments that contain Ranion ransomware executable files. Since Ranion is more suitable for general attackers, their ransomware has not been attacked by advanced attackers. This may also be why they have been able to continue operations for more than four years.
Ranion’s ransom information supports eight languages (English, Russian, German, French, Spanish, Italian, Dutch, and Persian) by default, and any region where these languages are mainly used can be the target of Ranion.
Does Ranion Ransomware imitate HiddenTear?
The world’s first open-source ransomware-Hidden Tear, its complete source code has been published on GitHub. This allows attackers to download source code and create their own ransomware variants to infect victims.
Since the source code is readily available, there are many ransomware variants with different names that use the same HiddenTear code base. Since the original code can be decrypted, this means that all other ransomware created with the same code can also be decrypted.
Ranion’s code is based on open-source proof-of-concept ransomware called HiddenTear. There are some code similarities between the two projects.

The screenshot above is from HiddenTear’s implantation of encryption functions. It can be found at https://github.com/goliate/hidden-tear/blob/master/hidden-tear/hidden-tear/Form1.cs. The implementation process of Ranion is as follows:
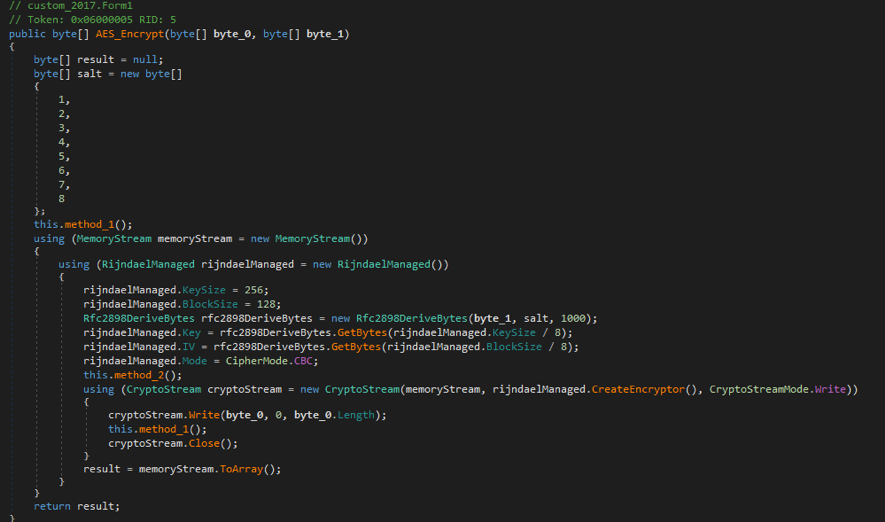
In order to encrypt files, HiddenTear uses this function.
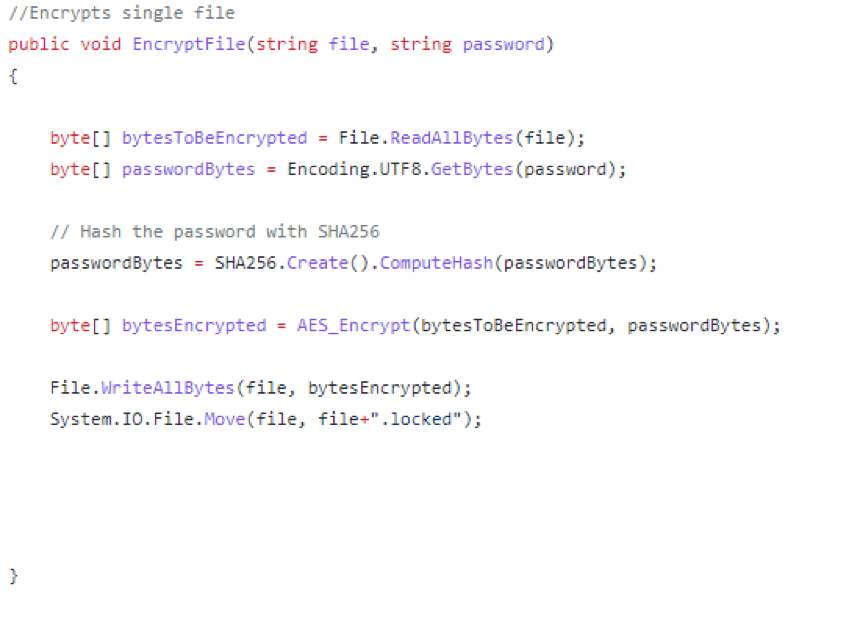
Ranion implements its encryption in a similar way.
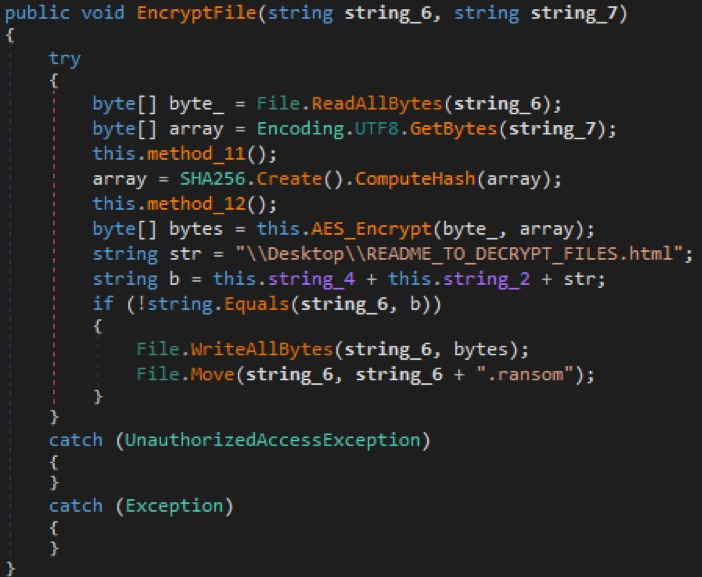
These are just two examples, and the similarities in overall programming can be seen in many places. In addition, Ranion’s resources are also similar to HiddenTear.
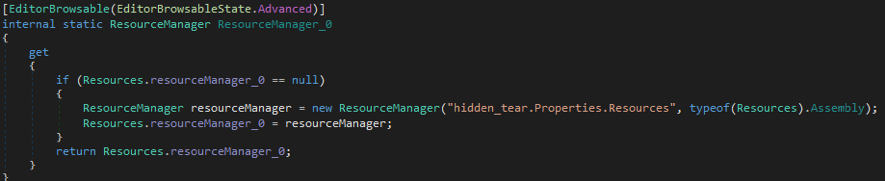
Note: This Ranion variant is from 2017 and its SHA256 hash value is eed03a9564aee24a68b2cade89d7fbe9929e95751a9fde4539c7896fda6bdcb5.
Become FFFFUUUUDDDD
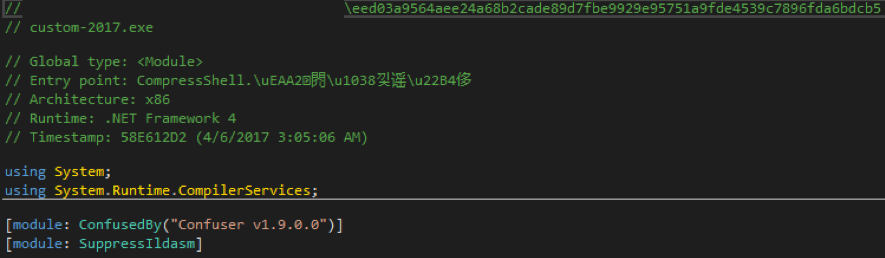
In order not to be discovered, the Ranion team has always relied on the ConfuserEx project, which is the successor of the now-defunct Confuser project. It is a free and open-source obfuscation program that “protects” .NET applications through symbol renaming, anti-debugging, encryption, compression, and other functions, making malware more difficult to analyze. The 2017 Ranion variant analyzed below is “protected” by the Confuser project.
The following Ranion 2021 variants have been “secured” using the ConfuserEx project.
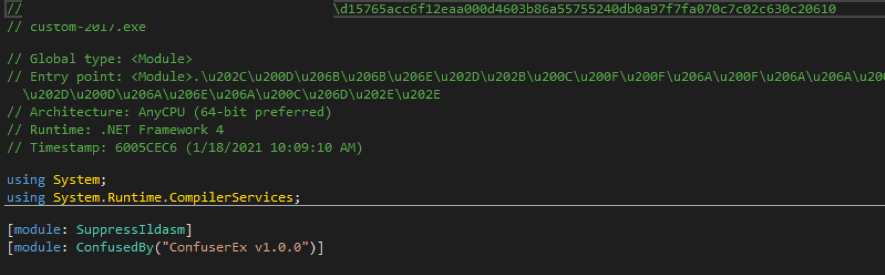
Although ConfuserEx is able to do what it says, that is, to “protect” .NET applications, in this case, it uses evasion techniques to protect malware from being detected by antivirus software.
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE






