A Threat Actor Creates Fake Advertising for Authenticator that Impersonates Google

A Threat Actor Creates Fake Advertising for Authenticator that Impersonates Google
We have previously reported on the problem of brand impersonation that occurs with Google AdWords. Users who search for popular keywords are presented with malicious advertisements that attempt to pass themselves off as coming from an authentic vendor.
As a result of this, not only does it fool innocent victims into downloading malware or losing their data to phishing sites, but it also erodes trust in brands and, by extension, in Google Search itself.
Here is yet another illustration of the misuse of a brand, with the exception that this particular instance is directed against Google itself. In the past few days, if you were attempting to download the well-known Google Authenticator, which is a multi-factor authentication tool, through a Google search, it is possible that you have unwittingly installed malware on your computer.
In the past, the sandbox manufacturer AnyRun found a distribution site that was comparable to the one in question, as well as an identical payload. This blog post will reveal the missing element at the top of the kill chain, which is the Google ad that was involved in deceiving viewers into visiting a decoy website. This piece will be revealed in this blog post.
Trust, but ‘verified’?
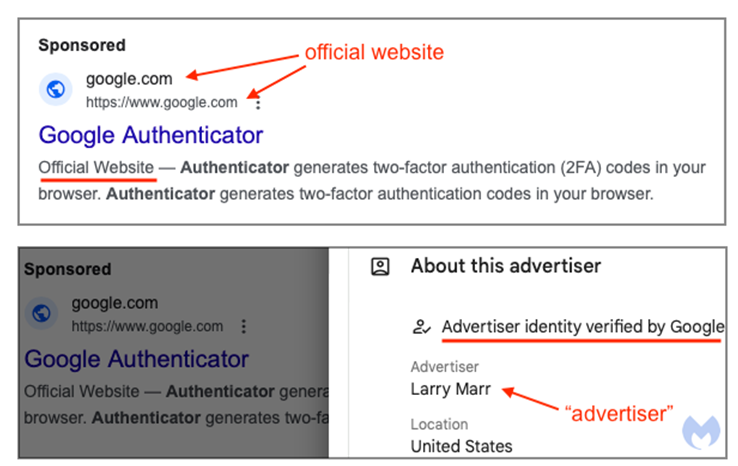
Advertisements that give the impression that they were obtained from official sources and advertisers whose identities have been verified by Google are the primary source of the problem of brand impersonation. When it came to this advertisement for Authenticator, this was the situation:
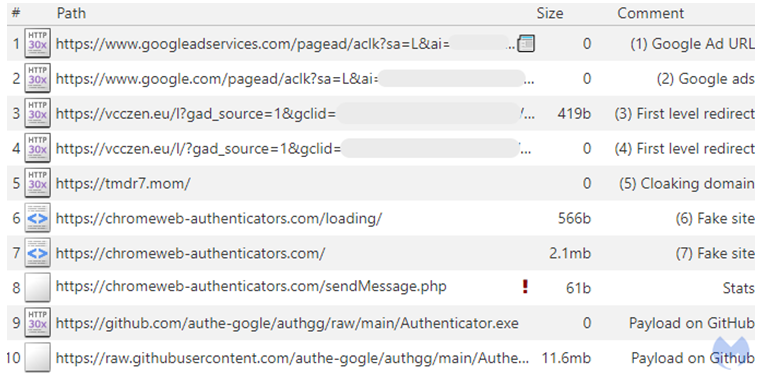
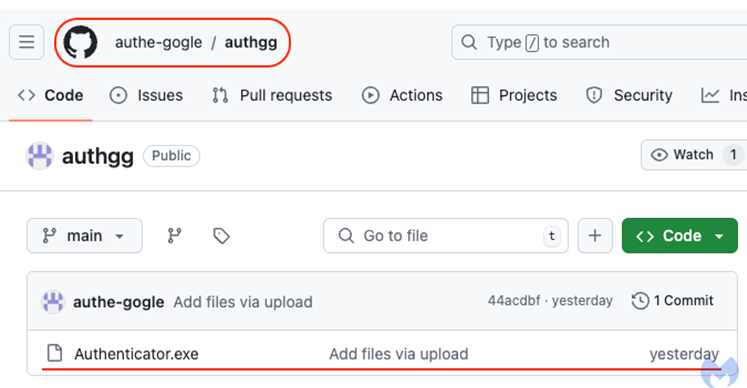
In reality, Larry Marr is not affiliated with Google in any way, and it is quite likely that his account is fake. By monitoring the traffic on the website, we are able to track what happens when you click on the advertisement. Before arriving at a phony website for Authenticator, we observe a series of redirections that are carried out through intermediary sites that are under the authority of the attacker.
Fake Site Leads to Signed Payload Hosted on Github
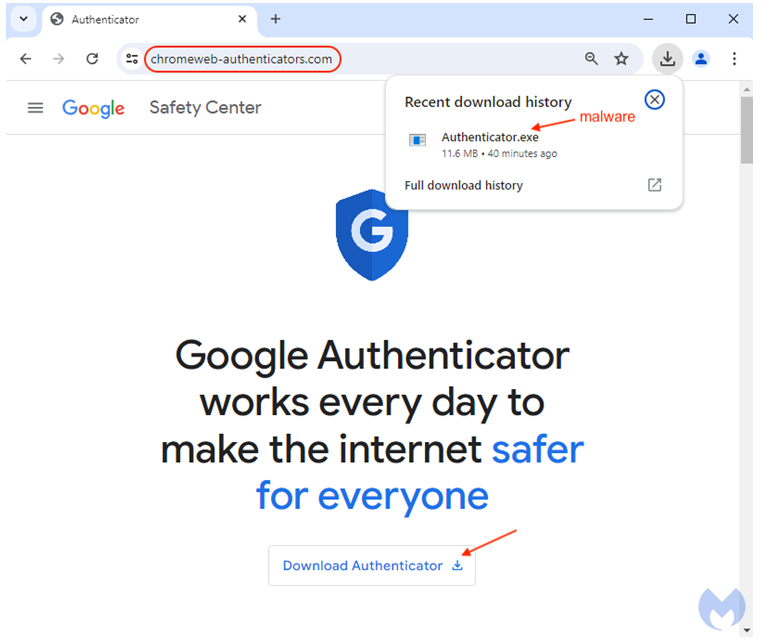
On the same day that the advertisement was seen, the fraudulent website chromeweb-authenticators[.]com was registered through NICENIC INTERNATIONAL GROUP CO., LIMITED.
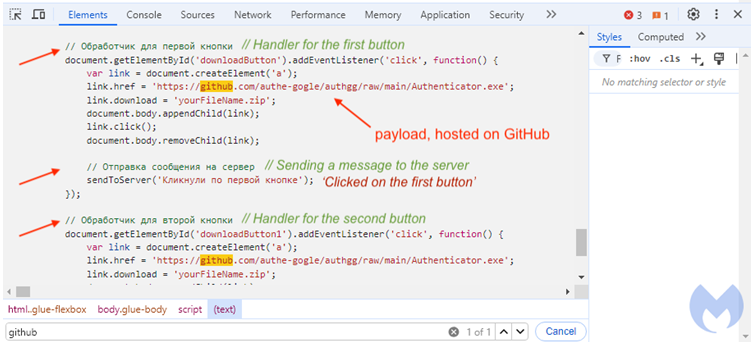
By examining the source code of the website, we are able to identify the code that is accountable for downloading Authenticator.exe from your GitHub repository. Take note of the opinions expressed by the author in Russian:
By hosting the file on GitHub, the threat actor is able to make use of a reliable cloud resource that is significantly less likely to be prevented using traditional methods. There are some programs and scripts that are hosted on GitHub that are not valid, despite the fact that GitHub is the de facto software repository. In point of fact, anyone is able to create an account and upload files, which is precisely what the threat actor did under the identity authe-gogle. They created the authgg repository, which is where the malicious Authenticator.exe file is located:
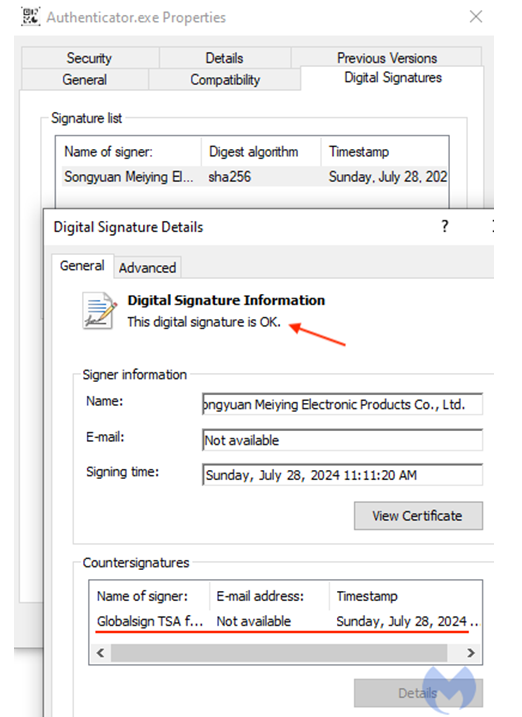
When we take a look at the file itself, we can see that it was digitally signed by “SongyuanMeiying Electronic Products Co., Ltd.” exactly one day prior to this writing, and the signature is still valid at the time of this writing:
The malicious software known as DeerStealer is a type of stealer that will take your personal information and then steal it from you by using a website that is managed by an attacker and hosted at vaniloin.fun.
About The Author:
Yogesh Naager is a content marketer who specializes in the cybersecurity and B2B space. Besides writing for the News4Hackers blogs, he also writes for brands including Craw Security, Bytecode Security, and NASSCOM.
READ MORE ARTICLE HERE